
Why Oats Deserve a Place on Your Plate
You already know oats offer a comforting breakfast. They’re also terrific in meatballs, quick breads, smoothies, and so much more. Oats are nutritious, too. They’re packed with nutrients and fibre that can support your well-being in many ways. Let’s take a look at what oats offer and how they promote good health.
What Oats Provide
Oats pack a nutritious punch:1
- High in fibre
- Plant-based protein
- Essential vitamins and minerals
- Antioxidants
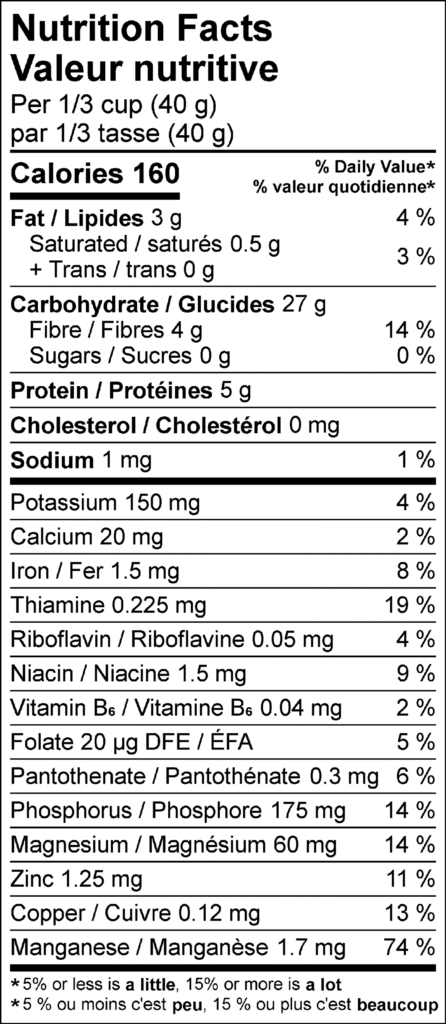
Nutrition Facts for Uncooked Large-flake Rolled Oats
| Title | Description | Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent Source of Manganese | Manganese supports immunity, bone strength, reproduction, and blood clotting.2 | 74% |
| Good Source of Thiamin | Thiamin (vitamin B1) is important for growth and development.3 | 19% |
| Source of Magnesium | Magnesium helps to keep your heart and blood pressure healthy.4 | 14% |
| Source of Phosphorus | Phosphorus supports bones and teeth.5 | 14% |
| Source of Copper | Copper supports the nervous and immune systems.6 | 13% |
| Source of Zinc | Zinc helps your body fight infections and heal wounds.7 | 11% |
| Source of Niacin | Niacin (vitamin B3) supports healthy cell growth and function.9 | 9% |
| Source of Iron | Iron helps your body grow and feel energized.8 | 8% |
| Source of Pantothenate | Pantothenate (vitamin B5) helps turn food into energy.10 | 6% |
| Source of Folate | Folate (vitamin B9) is used to make DNA.11 | 5% |
Types of Oats: Do They Have Different Nutrients?
All types of oats, including instant, quick, rolled, steel-cut, oat groats, and oat bran, are high in fibre, providing about 4 grams of fibre and 140 to 160 calories per 40-g (uncooked) serving. Oat flour (30 g) and Scottish oats (40 g uncooked) have slightly less, with 3 grams of fibre. Oat bran is slightly higher in iron and some B vitamins compared to standard oatmeal.
Serving Sizes are based on the Table of Reference Amounts for Food, Nutrition Labelling, Health Canada. Nutrient Values from Health Canada. Canadian Nutrient File, 2015.
How Oats Affect Blood Sugar
For people living with diabetes or looking to manage their blood sugar levels, it can be helpful to know that different types of oats affect blood sugar differently.
- Oat bran has a low glycemic index (GI), while steel-cut oats have a low-medium GI, meaning they raise blood sugar more slowly.12
- Quick and rolled oats are medium GI, and instant oats are high GI, so they raise blood sugar more quickly.12
Adding a protein source, like Greek yogurt or nuts, to a bowl of oatmeal can help to balance rises in blood sugar.
Good to know: Oats are naturally gluten-free. However, they may come into contact with gluten-containing grains such as wheat, rye, or barley during farming, transportation, storage, or processing.13 If you are avoiding gluten, choose oats labelled “gluten-free.” Find out more from Celiac Canada: Oats for People with Celiac Disease.
Find out more about different types of oats: “Know your Oats.”
5 Ways Oats Help Support Good Health
Oats are a tasty, budget-friendly staple that’s packed with nutrition, including vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants. They support wellness at every age, making them a smart choice for the whole family. Here are five powerful ways oats help keep you healthy.
Click on each for more information:
1. An Easy Way to Get More Iron
Just ⅓ cup (75 mL) of raw oats gives you 8% of your recommended daily iron, a mineral that’s especially important for growing kids, teen girls, and women.14, Iron helps carry oxygen through your body, keeping you energized and focused. To boost iron absorption, pair oats with meat, poultry, fish, or vitamin-C-rich foods like peppers or strawberries.15
Good to know: Kids who eat oatmeal for breakfast get more iron and other key nutrients, and tend to have better overall diets, than those who skip breakfast or eat other foods.16
In the kitchen: Oat flour has nearly twice the iron of whole-wheat flour.17 Try recipes made with oat flour, or swap it in to replace 25% to 50% of the whole-wheat flour in a recipe (start with 25% and increase as desired). Oat flour is great for pancakes, waffles, quick breads, muffins, and scones.
2. Support for Better Heart Health
Including oats as part of a healthy diet can support heart health in several ways. The soluble fibre in oats helps lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and steady blood sugar levels.18-19 The antioxidants in oats may reduce inflammation, and some of the compounds have been linked to lower blood pressure.20,21 Oats are low in saturated fat and free of trans fat.14 Together, these benefits make oats a powerful addition to a heart-healthy diet.
Good to know: Health Canada recognizes that beta-glucan, the soluble fibre in oats, can help lower cholesterol, so it permits a cholesterol-lowering claim on oats packaging. Just ⅓ cup (75 mL) of uncooked oats provides about half the daily amount needed for this heart-health benefit.22
In the kitchen: Getting ⅓ cup (75 mL) of dry oats daily is easy. Enjoy them in overnight oats and smoothies, or cooked up in a warm bowl of oatmeal.
3. Steady Energy Without the Spikes
Oats help keep blood sugar steady, a big win for health. Their soluble fibre slows carbohydrate digestion, reducing spikes and crashes.19,23 That means better blood sugar control, steadier energy, and less chronic inflammation. That’s helpful for people with prediabetes or diabetes, and for anyone who wants to feel good all day long.
Good to know: Pairing oats with a protein source can further slow digestion and keep blood sugar stable. Think overnight oats made with Greek yogurt, meatballs made with oats, or oat energy bites made with nut butter.
In the kitchen: Try this recipe for Chocolate Pumpkin Seed Oat Energy Bites. They need no cooking, they’re easy to make, and they can even be frozen or made into bars. And they’re absolutely delicious!
4. Fuel for a Healthier, Happier Gut
A healthy gut can impact everything from energy and mood to long-term disease risk.24 Oats contain both soluble and insoluble fibre, a combo that helps to keep you regular (reduces constipation) and the healthy bacteria in your gut thriving. These gut bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which early research suggests may help lower inflammation, boost immunity, and protect your heart and brain.1,25-27
Good to know: Most people get only half the fibre they need.28-30 Women need 25 grams daily, and men need 38 grams daily. Just ⅓ cup (75 mL) of uncooked oats gives you 4 grams of fibre.14
In the kitchen: An easy way to boost fibre intake is to add oats to meals beyond breakfast. Try this delicious “Jennifer Aniston” Salad made with gut-friendly, higher-fibre foods like steel-cut oats, chickpeas, and pistachios.
5. Support for a Healthy Weight
Oats can support weight management by helping you to get a lot of good nutrition with a modest number of calories per serving providing 140 to 160 calories per 40-g (uncooked) serving.14 Oats also help you feel full longer,31 making it easier to fuel your day without feeling the need to snack constantly.
Good to know: The beta-glucan fibre in oats slows digestion and boosts hormones that signal fullness to the brain. 32,33
In the kitchen: For a filling breakfast oatmeal bowl, start with plain cooked oats. Add flavour with cinnamon and vanilla extract, and build extra staying power with fresh fruit, a spoonful of nut butter, a sprinkle of chia or hemp seeds, or even a scoop of unsweetened protein powder.
Want to know more about fibre and oats?
- Fibre, Health Canada
- Fibre and whole grains, Heart and Stroke
- What Does Fibre do for Digestive Health?, Canadian Digestive Health Foundation
- All About Oats, Dietitians of Canada
- Canadian Ingredient Spotlight: Oats, Canadian Food Focus
References
View all
- Paudel D, Dhungana B, Caffe M, Krishnan P. A Review of Health-Beneficial Properties of Oats. Foods. 2021 Oct 26;10(11):2591.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements, National Institutes of Health, 22 Mar. 2021, ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Manganese-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2021, March 22). Thiamin – Consumer. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Thiamin-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2022, June 2). Magnesium – Health Professional. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2023, May 4). Phosphorus – Health Professional. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Phosphorus-HealthProfessional/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2022, October 18). Copper – Consumer. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Copper-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2022, October 4). Zinc – Consumer. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2023, August 17). Iron – Consumer. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2021, March 22). Niacin – Consumer. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Niacin-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2021, March 22). Pantothenic acid – Consumer. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/PantothenicAcid-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. (2022, November 1). Folate – Consumer. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-Consumer/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- University of Sydney Glycemic Index Research Service. (n.d.). GI Search. University of Sydney. https://glycemicindex.com/gi-search/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- Celiac Disease Foundation. (2024, April 11). Gluten-free oats: What’s the deal? https://celiac.org/gluten-free-oats-whats-the-deal/. Accessed 20 Aug. 2025.
- Nutrient values from Health Canada. Canadian Nutrient File, 2015. Food code 1464.
- Institute of Medicine. (2006). Iron. *Dietary reference intakes: The essential guide to nutrient requirements* (pp. 328–332). The National Academies Press.https://doi.org/10.17226/11537
- Fulgoni VL 3rd, Brauchla M, Fleige L, Chu Y. Oatmeal-Containing Breakfast is Associated with Better Diet Quality and Higher Intake of Key Food Groups and Nutrients Compared to Other Breakfasts in Children. Nutrients. 2019 Apr 27;11(5):964. PMID: 31035541
- Nutrient values from Health Canada. Canadian Nutrient File, 2015. Food Codes: oat flour (6275), whole-wheat flour (4500).
- Government of Canada. (2025, July 11). Summary of assessment of a health claim about oat products and blood cholesterol lowering. Health Canada. Retrieved August 21, 2025, from https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/food-labelling/health-claims/assessments/products-blood-cholesterol-lowering-summary-assessment-health-claim-about-products-blood-cholesterol-lowering.html
- Chen V, Zurbau A, Ahmed A, Khan TA, Au-Yeung F, Chiavaroli L, Blanco Mejia S, Leiter LA, Jenkins DJA, Kendall CWC, Sievenpiper JL. Effect of oats and oat ß-glucan on glycemic control in diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022 Sep 1;10(5).
- Paudel D, Dhungana B, Caffe M, Krishnan P. A Review of Health-Beneficial Properties of Oats. Foods. 2021 Oct 26;10(11):2591. PMID: 34828872.
- Liska DJ, Dioum E, Chu Y, Mah E. Narrative Review on the Effects of Oat and Sprouted Oat Components on Blood Pressure. Nutrients. 2022 Nov 11;14(22):4772. PMID: 36432463
- Health Claim derived from retail packaging for the brands (Quaker Oats: rolled oats, quick oats, steel cut). To make this health claim, the food must provide at least 0.75 g of oat beta‑glucan per Health Canada Reference Amount and per serving of stated size.
- Hou Q, Li Y, Li L, Cheng G, Sun X, Li S, Tian H. The Metabolic Effects of Oats Intake in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2015 Dec 10;7(12):10369-87. PMID: 26690472.
- Hills RD Jr, Pontefract BA, Mishcon HR, Black CA, Sutton SC, Theberge CR. Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease. Nutrients. 2019 Jul 16;11(7):1613. PMID: 31315227
- Xiong RG, Zhou DD, Wu SX, Huang SY, Saimaiti A, Yang ZJ, Shang A, Zhao CN, Gan RY, Li HB. Health Benefits and Side Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods. 2022 Sep 15;11(18):2863. PMID: 36140990
- Xu D, Feng M, Chu Y, Wang S, Shete V, Tuohy KM, Liu F, Zhou X, Kamil A, Pan D, Liu H, Yang X, Yang C, Zhu B, Lv N, Xiong Q, Wang X, Sun J, Sun G, Yang Y. The Prebiotic Effects of Oats on Blood Lipids, Gut Microbiota, and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Subjects Compared With Rice: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:787797.PMID: 34956218.
- Fabiano GA, Shinn LM, Antunes AEC. Relationship between Oat Consumption, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Synthesis: An Integrative Review. Nutrients. 2023 Aug 11;15(16):3534. PMID: 37630725.
- Ahmed M, Praneet Ng A, L’Abbe MR. Nutrient intakes of Canadian adults: results from the Canadian Community Health Survey (CCHS)-2015 Public Use Microdata File. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021 Sep 1;114(3):1131-1140. PMID: 34020449.
- Health Canada. Do Canadian Adolescents Meet Their Nutrient Requirements Through Food Intake Alone? 2012. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/food-nutrition-surveillance/health-nutrition-surveys/canadian-community-health-survey-cchs/canadian-adolescents-meet-their-nutrient-requirements-through-food-intake-alone-health-canada-2012.html
- Health Canada. Do Canadian Children Meet Their Nutrient Requirements Through Food Intake Alone? 2012. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/food-nutrition-surveillance/health-nutrition-surveys/canadian-community-health-survey-cchs/canadian-children-meet-their-nutrient-requirements-through-food-intake-alone-health-canada-2012.html#a323
- Rebello CJ, Johnson WD, Martin CK, Xie W, O’Shea M, Kurilich A, Bordenave N, Andler S, van Klinken BJ, Chu YF, Greenway FL. Acute effect of oatmeal on subjective measures of appetite and satiety compared to a ready-to-eat breakfast cereal: a randomized crossover trial. J Am Coll Nutr. 2013;32(4):272-279. PMID: 24024772.
- Shehzad A, Rabail R, Munir S, Jan H, Fernández-Lázaro D, Aadil RM. Impact of Oats on Appetite Hormones and Body Weight Management: A Review. Curr Nutr Rep. 2023 Mar;12(1):66-82. doi: 10.1007/s13668-023-00454-3. Epub 2023 Feb 15. PMID: 36790719.
- Mathews R, Shete V, Chu Y. The effect of cereal Β-glucan on body weight and adiposity: A review of efficacy and mechanism of action. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(19):3838-3850. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1994523. Epub 2021 Nov 3. PMID: 34727805.
Share your love for oats:
Download the “5 Powerful Ways Oats Boost Your Health” Infographic!

